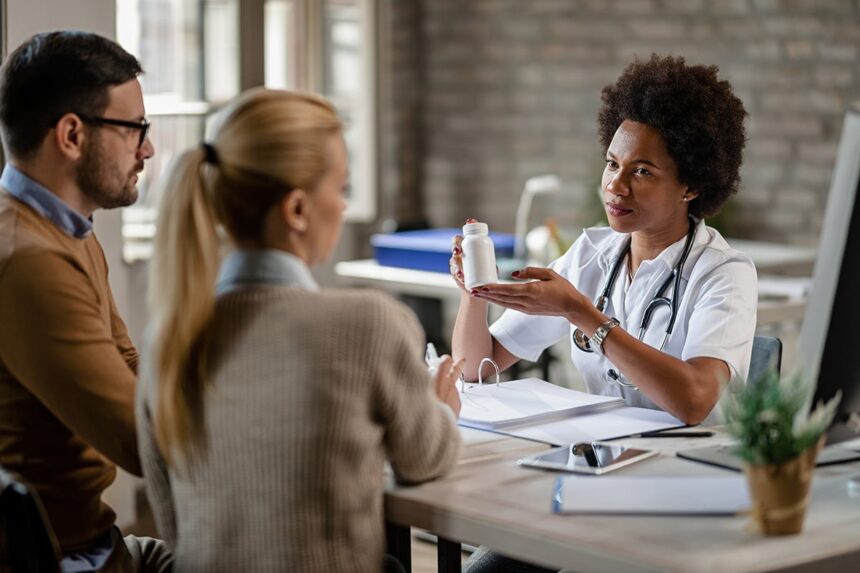
Introduction
Dengue fever, a mosquito-borne illness caused by the dengue virus, poses significant health risks in tropical and subtropical regions, including Florida and Jamaica. Both locales have recently experienced outbreaks that underscore the importance of awareness and preparedness. As we navigate these challenges, understanding the transmission, symptoms, and preventive measures against dengue is crucial. This blog aims to provide valuable insights and practical tips to help communities in Florida and Jamaica combat the spread of this potentially severe disease effectively. Together, we can foster resilience and optimism in the face of these health challenges.
Understanding Dengue Fever Outbreaks
 Image courtesy: Unsplash
Image courtesy: Unsplash
Overview of Dengue Virus in Florida
Dengue fever, predominantly transmitted by the Aedes aegypti mosquito, manifests significantly in subtropical climates, such as Florida’s. This region’s warm temperatures and frequent rainfall create ideal breeding grounds for mosquitoes, thereby facilitating the virus’s persistence and spread. Florida has witnessed both isolated and travel-associated dengue cases, with notable increases during the warmer months when mosquito activity peaks. Local health departments, particularly in mosquito-prone areas, actively monitor these outbreaks to implement control measures effectively. The campaigns focus not just on eliminating mosquito breeding sites but also on public awareness about the potential severity of the disease.
Impact of Jamaica Dengue Fever Outbreak
In Jamaica, dengue outbreaks have a profound impact on public health and the economy. The island has experienced several significant outbreaks, with the most severe ones prompting national alerts and straining healthcare resources. As a tourist haven, outbreaks can deter visitors, affecting the local economy heavily reliant on tourism. Government and health organizations prioritize educational programs, teaching locals and visitors alike about prevention strategies such as mosquito net usage and standing water management. Community efforts are crucial in these responses, highlighting the need for collective action in mitigating the spread of the disease.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Dengue Fever
Recognizing Symptoms of Dengue Fever
Distinguishing the symptoms of dengue fever is crucial for early detection and treatment, which can significantly impact the disease’s progression. Initial symptoms often include high fever, severe headaches, pain behind the eyes, joint and muscle pains, fatigue, nausea, and a distinctive skin rash that appears two to five days after the onset of fever. These symptoms can be mild or severe and sometimes are mistaken for those of the flu or other viral infections, making knowledgeable self-assessment and timely medical consultation vital.
Importance of Blood Tests for Diagnosing Dengue Fever
When it comes to diagnosing dengue fever, blood tests are essential tools. These tests look for the presence of the virus or antibodies produced in response to the virus. Medical professionals might use several types of tests such as Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) tests to detect the virus’s genetic material in the early stages of the disease or serology tests to detect antibodies in later stages. Early diagnosis via these methods helps in managing symptoms more effectively and can prevent the disease from progressing to more severe forms, including dengue hemorrhagic fever, which can be life-threatening.
Effects of Dengue Fever on Health
The health effects of dengue fever can range from mild to severe. While many people recover within a week or two, the disease can progress to dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome in more severe cases, conditions characterized by bleeding, blood plasma leakage, and low platelet count. These complications can lead to severe dehydration, sudden blood pressure drop, and even death if not treated promptly. Recovery from severe dengue might require hospitalization, intensive care, and fluid replacement therapy. Long-term, the experience can have a psychological and physical toll on survivors, with continued weakness and fatigue for weeks to months after recovery. Therefore, awareness, early detection, and immediate medical attention are paramount in ensuring favorable outcomes for those affected.
Prevention and Treatment of Dengue Fever
Dealing with dengue fever effectively involves both preventive measures to avoid the bite of the disease-carrying mosquitoes and treatments to manage the symptoms if infection occurs. Ensuring proactive prevention and timely treatment can significantly reduce the severity and spread of dengue fever.
Treatment Methods for Dengue Fever
There is no specific medication for curing dengue fever, which makes prevention all the more critical. However, the approach to managing the disease involves supporting the body’s immune system to fight the virus. Rest and hydration are key components, as dengue can cause severe dehydration due to high fever and vomiting. Pain relievers with acetaminophen are recommended to alleviate muscle soreness and fever; however, drugs such as aspirin and ibuprofen should be avoided as they can increase the risk of bleeding. For severe cases, such as dengue hemorrhagic fever, hospitalization is necessary where patients might receive IV fluids, blood transfusions, and platelet transfusions to manage significant complications.
Long-term Effects of Dengue Fever
While many recover fully from dengue, the disease can have lingering effects in some cases. Fatigue, depression, and anxiety can persist for weeks to months after recovery. Moreover, severe cases, particularly those that escalate into hemorrhagic fever, can result in long-term damage to the liver and other organs. Individuals who experience severe dengue are also at risk of developing weakened immune systems, making them more susceptible to other infections in the future.
Management of Dengue Symptoms
Managing symptoms effectively can alleviate the discomfort caused by dengue and prevent further health complications. Regular monitoring of body temperature and hydration levels is crucial. Keeping the patient in a well-screened room or under a mosquito net can help prevent the disease from spreading to others through mosquitoes. Additionally, intake of plenty of fluids to replace electrolyte loss and taking complete rest can expedite recovery. Consultation with a healthcare provider is essential for appropriate guidance and to monitor for any signs of complications.
Comparing Dengue Fever with Other Mosquito-borne Diseases
Mosquito-borne diseases share transmission vectors but can differ widely in terms of symptoms, severity, and geographic distribution. Comparing these can help in understanding their dynamics and implementing effective control measures.
Zika Virus and Dengue Fever Compared
Zika virus and dengue fever are transmitted by the same type of mosquito, Aedes aegypti, and share a common geographical range, which includes Florida and parts of the Caribbean like Jamaica. Symptoms of Zika are generally milder, involving fever, rash, joint pain, and conjunctivitis, and rarely lead to serious health complications. Dengue, however, can be life-threatening and typically causes high fever, severe headache, pain behind the eyes, and muscle and joint pain. A major point of difference is the associated risk of congenital effects in Zika; pregnant women infected with Zika have a risk of giving birth to babies with microcephaly and other brain malformations. Dengue, while severe, does not directly affect fetal development.
Risk Analysis for Travelers
Travelers to regions with active dengue and other mosquito-borne diseases should be particularly vigilant. Using mosquito repellent, wearing long-sleeved shirts and long pants, and staying in accommodations with effective mosquito control measures are crucial preventive steps. Prior to traveling, consulting travel advisories and getting updated information on local disease outbreaks can greatly simplify risk management. Vaccinations are available for some mosquito-borne diseases like yellow fever, but not for dengue or Zika, which makes prevention strategies all the more important. HinderedRotorKnowing the symptoms and the respective preventive and management strategies for each disease ensures better preparedness and response during travel.
Environmental Factors Affecting Mosquito Populations
Understanding the environmental factors that contribute to the proliferation of mosquito populations is key to managing outbreaks of diseases like dengue fever. Various elements such as temperature, rainfall, and natural disasters play significant roles in mosquito breeding and survival rates.
Mosquito Presence in Jamaica
In Jamaica, the warm climate and abundant rainfall create ideal conditions for mosquitoes to thrive. The Aedes aegypti mosquito, the primary transmitter of the dengue virus, prefers to breed in water collected in man-made containers and is highly adapted to living in close proximity to humans. Urban areas with dense populations and inadequate waste management practices exacerbate the situation, providing numerous breeding sites. Efforts to control the mosquito population are ongoing, but the challenge remains significant due to the favorable environmental conditions and the adaptability of this mosquito species.
Impact of Hurricanes on Mosquito Populations
The impact of hurricanes on mosquito populations is profound and can significantly increase the risk of mosquito-borne diseases. Hurricanes bring prolonged rainfall and flooding, which result in the collection of stagnant water—perfect breeding grounds for mosquitoes. Following a hurricane, the sudden surge in mosquito populations can lead to spikes in the spread of diseases such as dengue fever. For example, after Hurricane Irma struck in 2017, regions including Florida and the Caribbean saw a noticeable increase in mosquito populations.
Preventative measures such as eliminating standing water, using insect repellent, and implementing community-wide mosquito control programs become even more crucial in the aftermath of such natural disasters. Additionally, public health education on the importance of personal and community protection against mosquitoes is vital to prevent outbreaks post-hurricane. The community’s prompt response to control mosquito populations immediately after the water settles can be pivotal in preventing a major outbreak.
Practical Tips for Prevention and Control
 Image courtesy: Unsplash
Image courtesy: Unsplash
Prevention Techniques for Mosquito Bites
Reducing your risk of dengue begins with effective mosquito bite prevention. Use insect repellent containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus on exposed skin, adhering to the instructions on the product label. Wearing long-sleeved shirts and long pants, especially during peak mosquito hours (from dawn to dusk), provides an additional layer of protection. Also, utilize mosquito nets while sleeping, especially if you are in an area with a high rate of dengue transmission.
Role of Housing in Mosquito Prevention
Your living environment plays a crucial role in mosquito control and, consequently, dengue prevention. Ensure that window and door screens are intact to prevent mosquitoes from entering your home. Regularly empty and clean containers that hold water, such as bird baths, plant saucers, and pet water dishes, to eliminate mosquito breeding sites. Air conditioning also helps as mosquitoes tend to avoid cooler temperatures, so keeping your home air-conditioned and closed can further reduce the risk of indoor mosquito bites.
Mosquito Population Variation in the Caribbean
The Caribbean, including Jamaica, experiences significant variation in mosquito populations due to its tropical climate, which can affect dengue transmission rates. During the rainy season, typically from May to October, there is a spike in mosquito populations due to the increased availability of breeding sites. Awareness and proactive mosquito control measures during these months are vital to reducing the risk of dengue. Community efforts, such as cleanup campaigns to remove stagnant water, can significantly help in controlling mosquito populations.






I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.